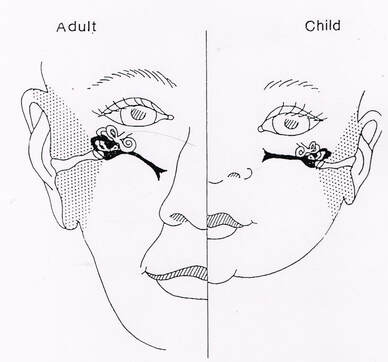
Why do children get otitis media?
It’s all about the eustachian tube........
|
Notice the ADULT eustachian tube is mature and sloping at a 45 degree angle for secretions to drain.
|
Children get middle ear problems because their eustachian tube (pronounced ‘you-stay-shun’) is immature and does not allow air into the middle ear properly.
The eustachian tube keeps the middle ear healthy by allowing little puffs of air to enter unnoticed during the day, most often when swallowing.
This is why it is SO IMPORTANT for children to blow their nose, fully clearing one side at a time.
Nose blowing allows air into the middle ear.
The eustachian tube keeps the middle ear healthy by allowing little puffs of air to enter unnoticed during the day, most often when swallowing.
This is why it is SO IMPORTANT for children to blow their nose, fully clearing one side at a time.
Nose blowing allows air into the middle ear.
Why is the eustachian tube so important?
|
The eustachian tube has 3 functions.
1) to allow air to pass up or down the tube which keeps the air pressure equal on both sides of the eardrum. 2) to allow middle ear secretions to drain down the tube into the nose. 3) to prevent the reflux (flow) of fluid back up the tube into the middle ear. Normal middle ear function relies on normal eustachian tube function. The eardrum can only vibrate normally when the ear canal and the middle ear are both full of air. |
Other interesting facts about the Eustachian Tube
- The eustachian tube is normally closed and only opens momentarily during swallowing and yawning. We normally swallow several times a minute while awake and once every 5 minutes while asleep.
- Eustachian tube function improves as children grow, around age 8-9 years. This is one reasons why otitis media is less common as children get older as the eustachian tube moves to a 45 degree angle.
- You are frequently aware of the eustachian tube when your ear ‘pops’ during swallowing or nose blowing, or when you ‘hear yourself talking’ in your ear during a yawn.
- When an airplane is landing, many people attempt to relieve middle ear pressure by blowing their nose while it is pinched shut to send air up the eustachian tube.
- During a cold or allergy attack, your ear may feel congested or ‘stuffy’ because the lining of the eustachian tube swells up and blocks off the flow of air.